What are the differences between mainstream display technologies?

Regarding screen display technologies, you may often hear professional terms such as LCD, OLED, Mini LED, and Micro LED, but it's always confusing to figure out the differences between them.
These technologies vary significantly in principles, effects, costs, and application scenarios. When choosing a screen, understanding their characteristics and differences will help make a decision that meets your own needs.
1
The principles of display technologies for different screens
The development of screen display technology has gone through multiple stages, from the earliest CRT displays to the current LCD, OLED, Mini LED, Micro LED and other technologies. Each display technology has its unique advantages.
LCD: The "common face" in display technology
Among all display technologies, LCD is the most common one. Its presence can be seen everywhere, whether in mobile phones, TVs, or advertising screens.
In principle, an LCD screen is a technology that uses liquid crystal molecules to change light transmittance under the action of an electric field. The liquid crystal itself does not emit light; instead, it relies on a backlight source to provide light. The liquidcrystal molecules adjust the amount of light passing through, and finally form an image.
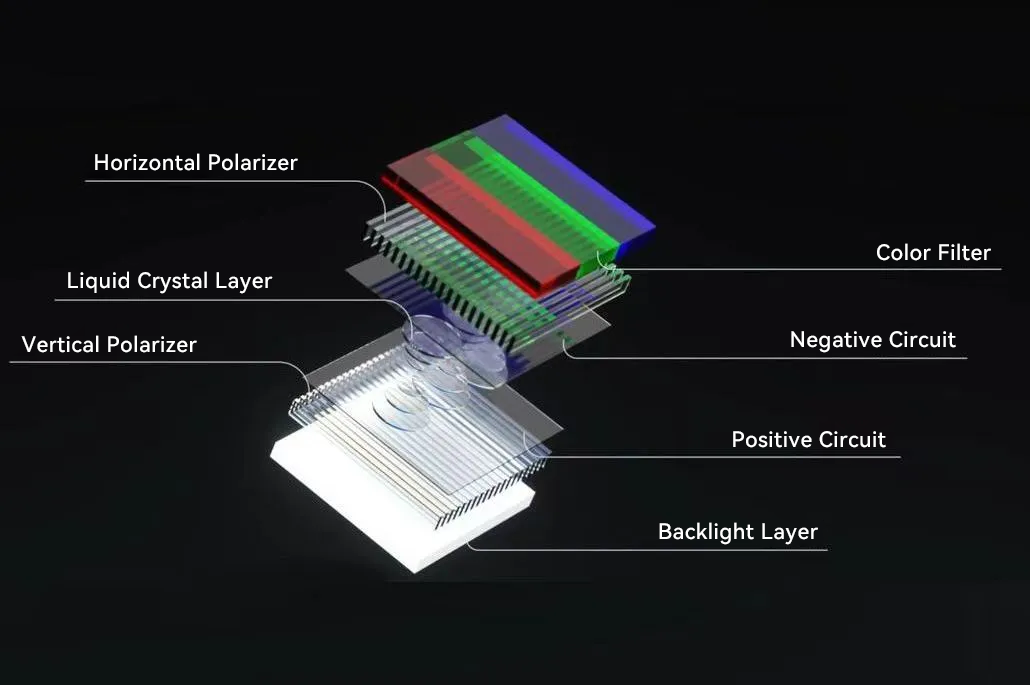
Schematic diagram of the structure of LCD display technology.
Compared with traditional CRT displays, LCD screens are small in size, light in weight, easy to move and install. Their thin design allows them to be easily adapted to places with limited space (such as shelves and countertops).

OLED: Flexible and bendable like "paper"
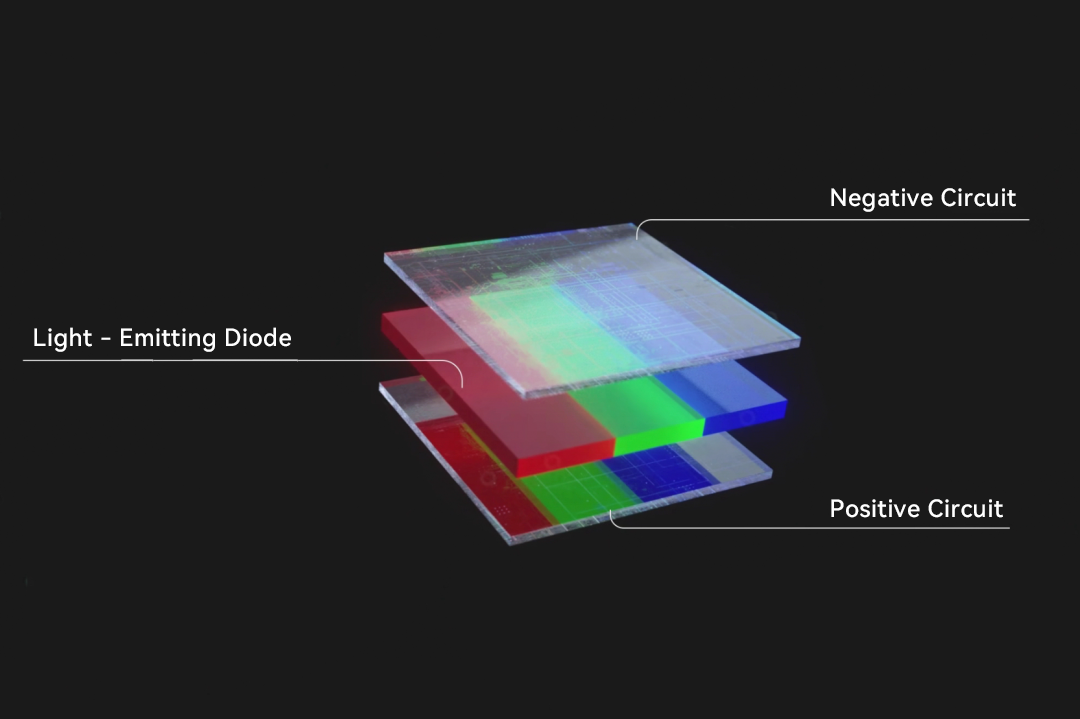
Schematic diagram of the structure of OLED display technology.
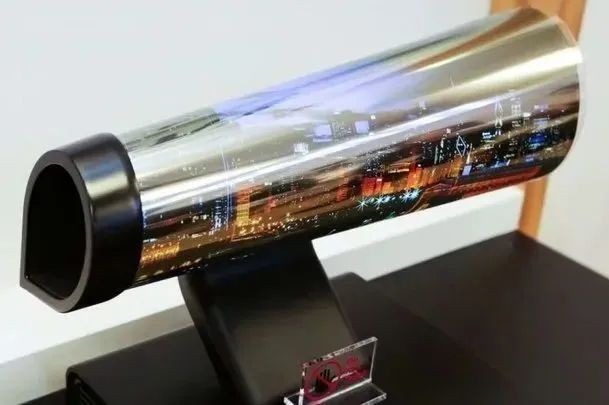
OLED does not use traditional glass panels but adopts flexible materials as the substrate, which can withstand certain deformations, so that screens of different shapes can be made, such as curved, folded, rolled and so on.

Mini LED: The "light regulator" with precise control
Mini LED technology further miniaturizes the backlight of LCD and has a large number of built - in tiny LED lamp bead groups that can be independently controlled to turn on and off.

Different areas in the screen can adjust brightness and contrast according to the needs of the content, so as to obtain more real and vivid visual effects.
When displaying dark scenes, Mini LED can effectively reduce the background brightness, and when displaying bright scenes, it can increase the brightness, making the image more delicate and vivid.
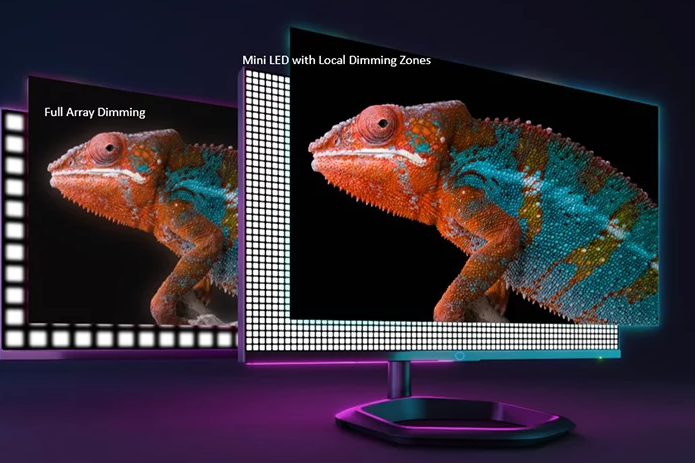

The more independently adjustable dimming zones there are, the better the color, contrast and HDR display effects will be.
Micro LED: The "innovator" in the display industry
Unlike OLED, Micro LED uses inorganic materials instead of organic materials. Therefore, each pixel is composed of a micro LED chip, and each chip can emit its own light.

Because the size of the micro LED chips used is extremely small, usually only a few tens of microns, the Micro LED display panel can be made thinner and lighter, and supports higher resolution and larger - sized screens.
2
Trade-offs: Image Quality, Budget and Maintenance
For most people, the principle of display technology is abstract. When choosing a screen, it is more based on needs at different levels. Among them, image quality, budget, installation and maintenance are all extremely critical factors to consider.
Visual experience: From ordinary image quality to extreme performance
In terms of color performance, Micro LED and OLED have absolute advantages. Because each pixel emits light independently, the colors are bright and accurate. Even in a dark background, the brightness of other parts will not be affected, the details in theimage are richer, and the overall picture is more layered.

A screen with independent control has richer and more delicate colors.
In contrast, OLED is more suitable for indoor environments with relatively dark light. When viewed outdoors or under direct sunlight, the picture may be unclear.

In terms of dynamic performance, Micro LED and OLED have extremely fast response times, with almost no motion blur and trailing.
Due to the characteristics of backlight adjustment, the response time and motion clarity of Mini LED are not as good as those of OLED, but it performs well in dynamic performance.
Budget considerations: From high cost - effectiveness to high investment
Although its image quality is not as good as that of other display technologies, its basic display functions are sufficient to meet daily use needs.

iMGS LCD screen series.
If you pay attention to a more extreme picture and have a sufficient budget, Micro LED screens are a better choice. They have extremely high resolution and seamless splicing characteristics, and can maintain delicate image quality on large - sized screens.

From a budget perspective, OLED screens are a lower - end alternative to Micro LED. They are inferior to Micro LED in terms of brightness, service life and screen burning problems, but within a budget lower than that of Micro LED, you can still get a good audio - visual experience.
Installation and maintenance: From integration to modularization
Because of its simple and mature structure, LCD technology almost has no screen burning problem, and the service life of the backlight is long, which can maintain stable performance under long - term use.

iMGS KT screen series can be moved to various corners at will.
OLED screens are thinner and softer than LCD screens. During installation, if they are subjected to uneven support or external pressure, the screen panel may be damaged.
In terms of durability, because each pixel of the OLED screen emits light independently, there is a probability of screen burning when displaying static images for a long time, so it is not suitable for applications that need to display static images for a long time.
OLED screens are mostly used in devices such as home TVs and smart phones.
Because Mini LED uses traditional backlight technology instead of self - luminous pixels, the brightness of each pixel will not degrade over time. It performs very well in long - term use, especially in preventing screen burning, which is better than OLED.

Compared with ordinary LCD screens, Mini LED requires more assembly and debugging work to ensure uniform backlight and no defects.
Micro LED usually adopts a modular design. The display panel is composed of multiple micro LED modules, and these modules need to be accurately docked and combined during installation.
Especially in large - sized displays or spliced display systems, a small error may affect the overall effect.

The modular installation of Micro LED requires very high precision to ensure that each module is seamlessly connected and avoid seams or color differences.
When faced with different display technologies, the final purchase decision often depends on one principle: before purchase, obtain the best visual effect within the budget; after purchase, consider the difficulty of screen installation and whether it is durable.





